Auto Checks: GitHub
Auto Checks for GitHub enable automated detection of misconfigurations in your GitHub environment, helping you ensure your organization follows a secure development lifecycle (SDLC). The checks are mapped to ISO 27001:2022 controls and curated with auditor input to help your organization continuously validate its compliance posture across critical repository settings.
This feature provides visibility into key areas like access management, change control, and secure development, transforming manual, time-consuming verification into an automated and structured process within Kertos.
How It Works
How to activate Auto Checks for GitHub in Kertos?
Steps to enable Auto Checks for GitHub:
- Go to the Integrations Page.
- Click Setup on the GitHub Integration card.
- If the integration is already active, click Reconfigure.
- Toggle Auto Checks ON if its disabled.
- Click button "Sign in with GitHub"
- Select where you want to install the App
- Select which Repos should be scanned
- Click Save in Kertos.
- Start a discovery run by clicking Start Scan.
Once the scan is completed, relevant Auto Checks for your GitHub repositories will be linked automatically in the Tab "Controls" to the corresponding controls and implementation steps in your compliance frameworks.
You can find all Auto Checks listed also in the Tab "Auto Checks".
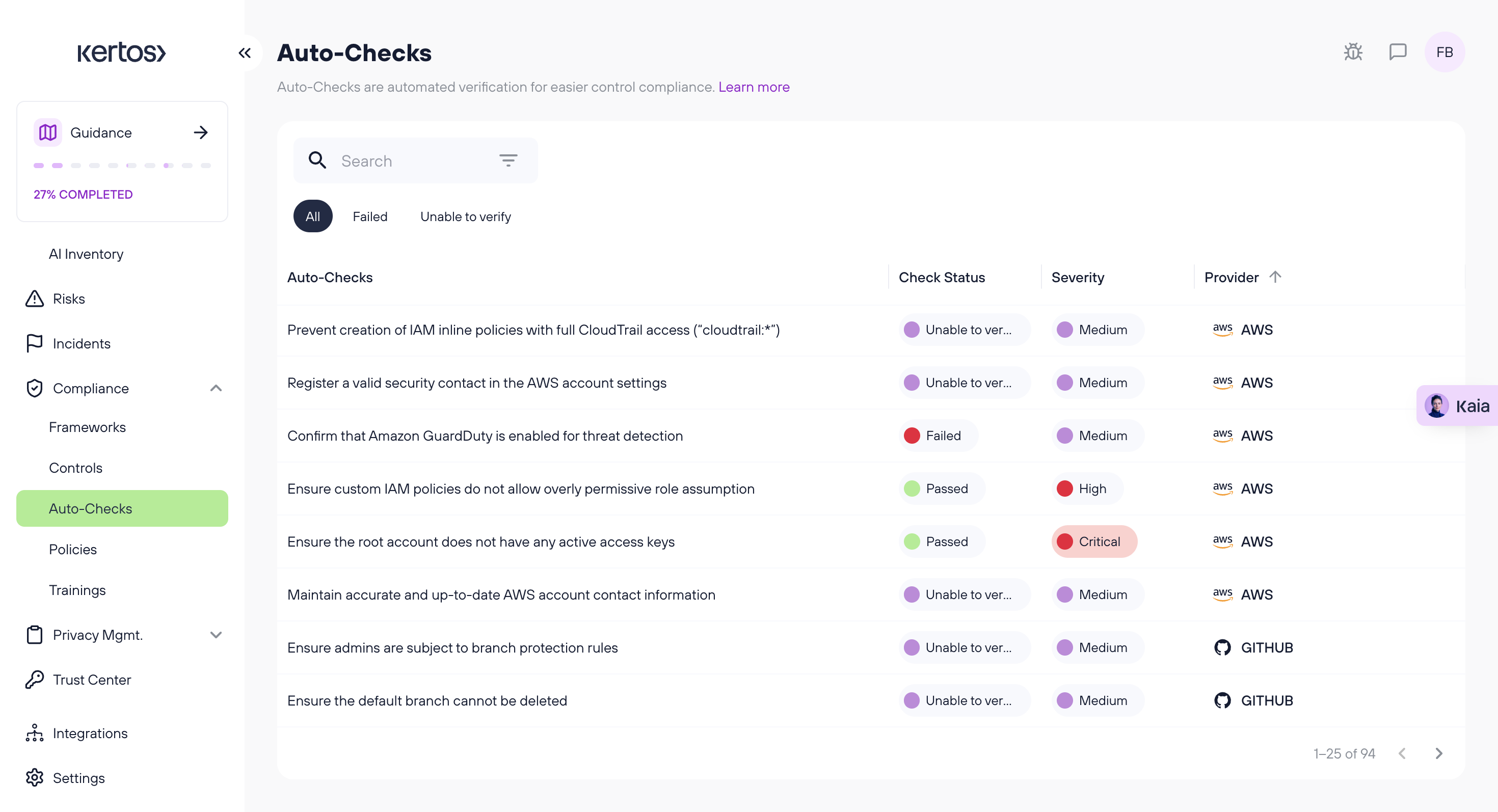
What Are the GitHub Auto Checks Based On?
The GitHub Auto Checks are based on widely recognized industry best practices for a Secure Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC).
In close collaboration with auditors, we curated a selection of the most relevant checks for security and compliance. Each check is aligned with ISO 27001:2022 controls to provide clear audit evidence and actionable remediation guidance for misconfigurations.
Which Auto Checks are available for GitHub, and how are they mapped to ISO 27001:2022 controls?
Each Auto Check is mapped to a specific ISO 27001:2022 control, helping to demonstrate technical implementation of key security requirements.
| ISO Control ID | ISO Control Title | Auto Check Title |
|---|---|---|
| A.8.5 | Secure authentication | Ensure all organization members have MFA enabled |
| A.8.9 | Configuration management | Ensure branches are deleted automatically after merging |
| A.8.3 | Information access restriction | Ensure the default branch cannot be deleted |
| A.8.3 | Information access restriction | Ensure force push is disabled for all branches |
| A.8.3 | Information access restriction | Ensure admins are subject to branch protection rules |
| A.8.3 | Information access restriction | Ensure branch protection is enforced on the default branch |
| A.8.25 | Secure development life cycle | Ensure code owner approval is required for owned code changes |
| A.8.25 | Secure development life cycle | Ensure unresolved conversations block merges |
| A.8.25 | Secure development life cycle | Ensure linear history is enforced on the default branch |
| A.8.25 | Secure development life cycle | Ensure at least two approvals are required before merging code |
| A.8.25 | Secure development life cycle | Ensure only signed commits are accepted |
| A.8.25 | Secure development life cycle | Ensure all required status checks pass before merging |
| A.8.8 | Management of technical vulnerabilities | Ensure vulnerability scanning is enabled for repository dependencies |
| A.8.25 | Secure development life cycle | Ensure a CODEOWNERS file exists in the repository |
| A.8.9 | Configuration management | Ensure inactive repositories are archived |
| A.8.25 | Secure development life cycle | Ensure public repositories include a SECURITY.md file |
| A.8.16 | Monitoring activities | Ensure secret scanning is enabled to detect sensitive data |
How to Uninstall the Kertos App from GitHub
Prerequisites: You must be an administrator for your GitHub organization.
Procedure
- In GitHub, navigate to your organization's page.
- Go to Settings. In the left sidebar under "Integrations," click Applications.
- In the "Installed GitHub Apps" tab, find the Kertos application and click Configure.
- Scroll to the bottom of the settings page to the Danger Zone section.
- Click the Uninstall button and confirm the action when prompted.
This is a common troubleshooting step used before re-connecting the integration to resolve a connection error.
How to Change GitHub Repository Access for Kertos
Prerequisites: You must be an administrator of your GitHub organization.
Procedure
- In GitHub, navigate to your organization's settings page.
- In the left sidebar, go to Settings > Integrations > Applications.
- Find the Kertos app in the list and click Configure.
- Scroll down to the Repository access section.
- From here, you can either add or remove repositories:
To Add a Repository:
In the "Select repositories" dropdown menu, search for and select the repository you want to add.
To Remove a Repository:
In the list of currently enabled repositories, click the X next to the repository you want to remove.
Finally, click the green Save button to apply your changes. The updated repository list will be reflected in Kertos after the next sync.
FAQs
What GitHub settings are currently supported? We currently support Auto Checks for critical GitHub security settings, including branch protection rules, organization-wide two-factor authentication (2FA) enforcement, repository admin privileges, and secret scanning (vulnerability alert) status.
Can I disable Auto Checks for GitHub? Yes. Go to the GitHub integration in Kertos, click Reconfigure, and toggle Auto Checks off.
Does this work with personal GitHub accounts? No. Auto Checks for GitHub can only be enabled for GitHub Organizations. The feature requires organization-level permissions to properly scan repository settings, security configurations, and member access. Personal accounts do not have the same structure and are not supported.
